Set up XDebug¶
XDebug is an extension for PHP that will help us with code debugging. We’ll use it combined with PHP Storm, which will provide us the step debugging feature, i.e. enable us to break during the code execution, inspect the variables in scope and evaluate code in the Console.
Install¶
MacPorts install¶
MacPorts provide multiple ports for installing XDebug, based on the PHP version you’re using. So, to check your version, execute on the command line:
php -v
and select the appropriate port from the list found here.
For example, if your PHP version is 7.4, you’ll need to execute
sudo port install php74-xdebug
Now, when executing
php -v
among other data, you should see XDebug in the output. Just by this
setup you already have some XDebug benefits, such as that var_dump()
function will now be upgraded to have a nicer output. But to fully
benefit XDebug, it is wise to add few more adjustments to configure step
debugging and connect it to PhpStorm.
Configure PHP¶
Depending on XDebug version you’re configuring, add the following lines
to php.ini: - XDebug3 and higher
xdebug.mode=debug,develop
- XDebug2 or under:
xdebug.remote_enable=1
xdebug.default_enable=0
xdebug.profiler_enable=0
xdebug.auto_trace=0
xdebug.coverage_enable=0
If you’re not sure which php.ini file to edit, you can check that by
executing
php --ini
Make sure you restart PHP-FPM server after making these changes. If you followed this development setup, then reload commands should look something like this on Mac:
sudo port reload php74-fpm
or like this on Ubuntu:
sudo systemctl reload php7.4-fpm
Configure XDebug on PhpStorm¶
Open
Preferences/Languages and Frameworks/PHP.Add your CLI interpreter here by opening CLI Interpreters window: inside it, click on plus sign and select Other Local…
Now you’ll need to adjust the PHP executable file path. If you’re unsure where your current PHP version executable file is, simply execute:
which phpand it will give you the path to the needed file.If everything is done correctly, PhpStorm should now list your PHP version, XDebug as debugger and PHP configuration file, looking something like this:
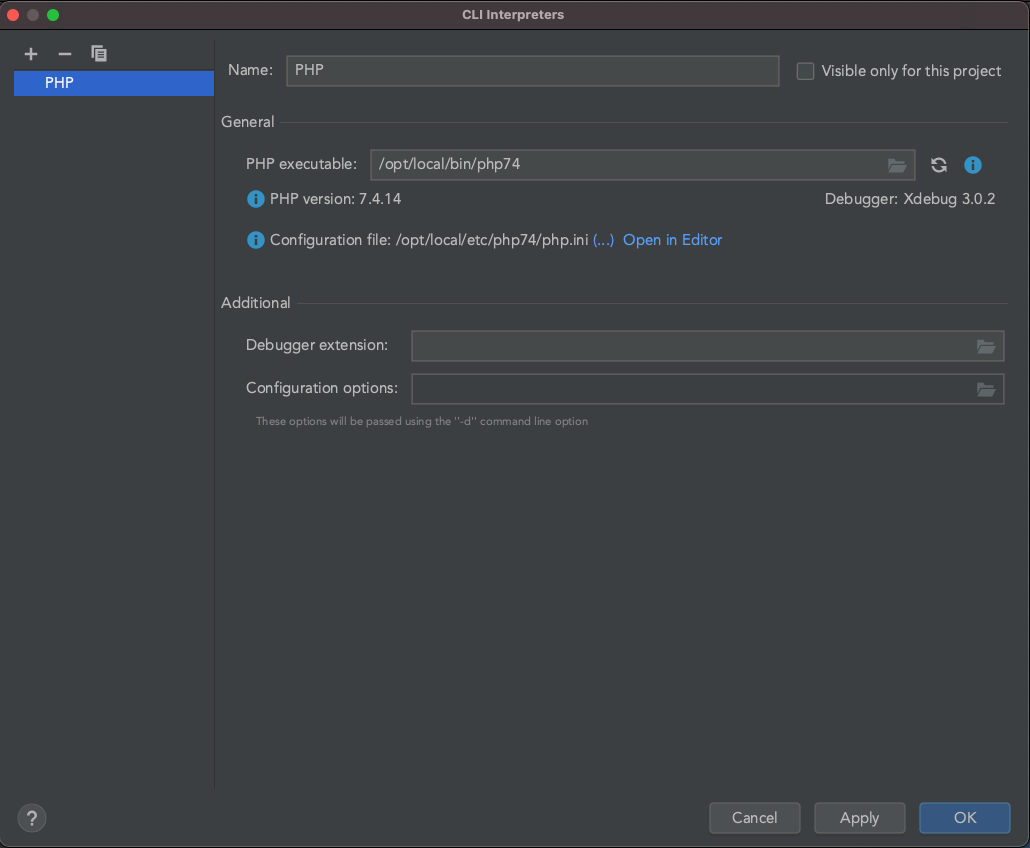
PhpStorm XDebug config
Skip this step if using XDebug version 2 or below (default port on these versions is 9000 so no adjustment is needed).
Next, we need to adjust debug port to 9003 which is the default XDebug port. Do so by going to
Preferences/Languages and Frameworks/PHP/Debugand setting Debug port under XDebug to 9003.In the end we just need to start listening to debug connections: enable
Run/Start Listening for PHP Debug Connectionsin the menu bar or use the shortcut button with the phone icon on the top right side of PhpStorm window.
Activating debugger¶
The easiest way for activating debugger is by installing XDebug Helper browser extensions. Choose your favorite browser, install and configure extension, and you’ll be able to start and stop debugging mode in your browser with just a few clicks. - XDebug Helper for Firefox - XDebug Helper for Chrome - XDebug Helper for Safari
Alternatively, if you want to activate the debugger manually, you’ll
need to add a trigger to your requests. Depending on what you need, add
one of the following: - XDEBUG_SESSION=session_name as an additional
GET (or POST) parameter if you want to initiate debugging on that single
request - XDEBUG_SESSION=session_name as a cookie: debugging will
now be initiated as long as that cookie is present
(value of session_name here is not important, you can set it to
whatever you like)
Test¶
Finally, choose a request you want to debug, set a breakpoint in PhpStorm on the line in your code you’re sure that your request will hit and fire away. If everything went well, PhpStorm should have opened debug window and now you have complete insight in what is happening in your code.
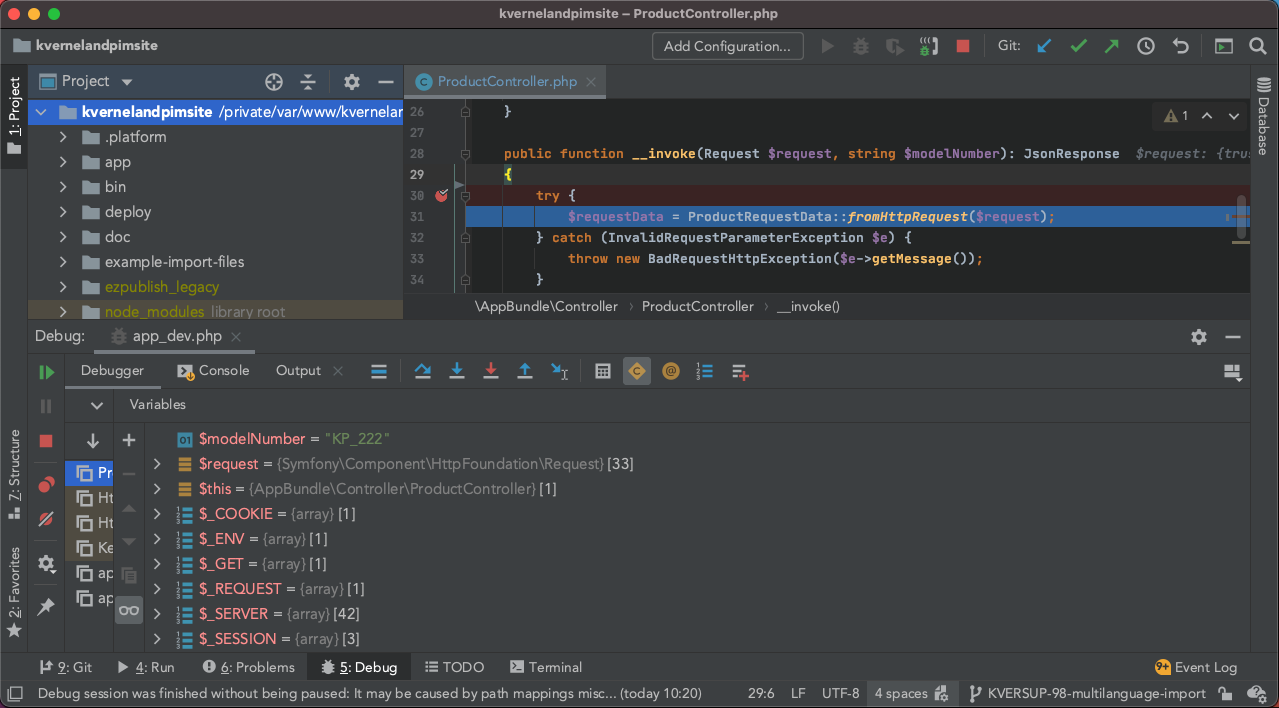
PhpStorm debug window
Easily enable and disable XDebug¶
To prevent XDebug slowing down our requests when we are not debugging, it would be wise to disable it whenever we’re not using it. That’s why we’ll guide you to write a few shell scripts and aliases with which XDebug enabling or disabling will be a matter of entering a three-letter command in terminal.
What we’ll want to do is rename xdebug.ini file so that it can’t be
found and hence won’t be loaded, and after that reload PHP-FPM server.
Again, as an example, everything will be done for PHP 7.4 so don’t
forget to adjust commands to your version.
MacOS configuration¶
Execute the following in the console:
cd /usr/local/bin
sudo vim disable-xdebug-74.sh
In the Vim editor, paste the following code:
#!/usr/bin/env bash
mv /opt/local/var/db/php74/xdebug.ini /opt/local/var/db/php74/xdebug.ini.disabled
port reload php74-fpm
echo "xdebug is now disabled"
Save and exit Vim.
We just created our script for disabling XDebug. Let’s also create a one for enabling it. Execute:
sudo vim enable-xdebug-74.sh
Here, paste:
#!/usr/bin/env bash
mv /opt/local/var/db/php74/xdebug.ini.disabled /opt/local/var/db/php74/xdebug.ini
port reload php74-fpm
echo "xdebug is now enabled"
and again, save and exit. After doing this, you should be able to enable and disable XDebug by executing one of the commands:
sudo sh /usr/local/bin/enable-xdebug-74.sh
sudo sh /usr/local/bin/disable-xdebug-74.sh
To make this even more simple, you can also create aliases for these commands. To do this, execute:
cd ~
vim .zshrc
Add the following lines to your .zshrc file:
alias exd74='sudo sh /usr/local/bin/enable-xdebug-74.sh'
alias dxd74='sudo sh /usr/local/bin/disable-xdebug-74.sh'
(exd74 and exd74 here can be any other alias you like: feel free
to use what suits you best)
By doing this, you can now enable XDebug simply by executing exd74
and disable it by executing dxd74.